Multi-Scale Fusion for Improved Localization of Malicious Tampering in Digital Images
Paweł Korus and Jiwu Huang
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, Vol. 25, Issue 3, 2016
2016-tip-multiscale-jpeg.pdf (2 MB)
https://github.com/pkorus/jpeg-mbfdf-forensics
Abstract
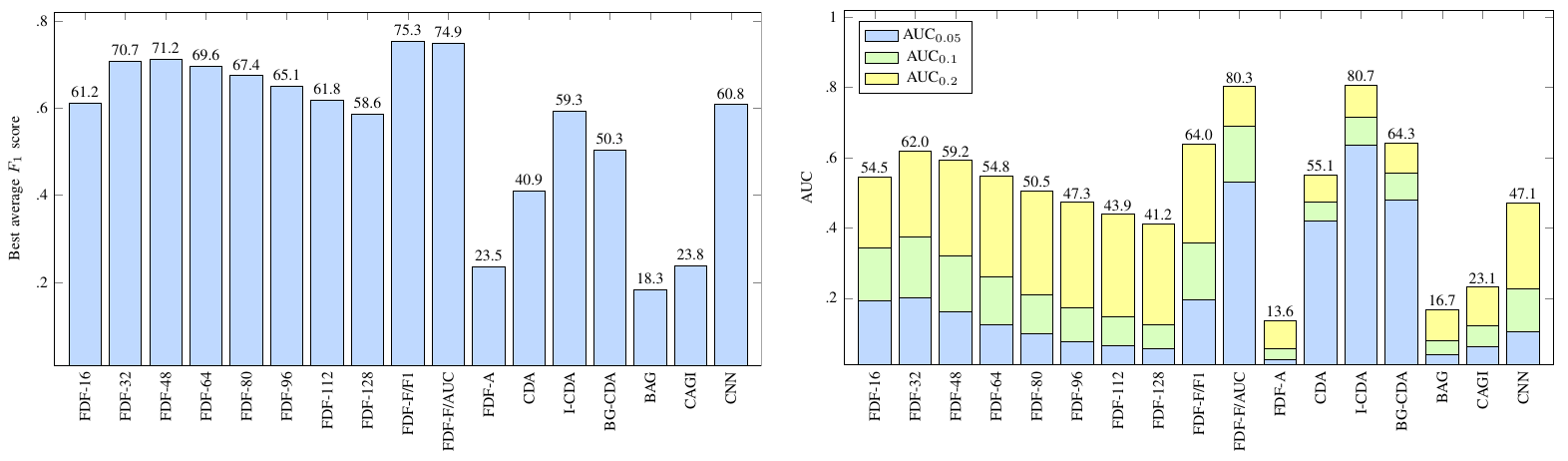
Sliding window-based analysis is a prevailing mechanism for tampering localization in passive image authentication. It uses existing forensic detectors, originally designed for full-frame analysis, to obtain the detection scores for individual image regions. One of the main problems with window-based analysis is its impractically low localization resolution stemming from the need to use relatively large analysis windows. While decreasing the window size can improve the localization resolution, the classification results tend to become unreliable due to insufficient statistics about the relevant forensic features. In this study, we investigate a multi-scale analysis approach which fuses multiple candidate tampering maps, resulting from the analysis with different windows, to obtain a single, more reliable tampering map with better localization resolution. We propose three different techniques for multi-scale fusion, and verify their feasibility against various reference strategies. We consider a popular tampering scenario with mode-based first digit features to distinguish between singly and doubly-compressed regions. Our results clearly indicate that the proposed fusion strategies can successfully combine the benefits of small-scale and large-scale analysis and improve the tampering localization performance.
Copyright
Copyright © 2015 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to use this material for any other purposes must be obtained from the IEEE by sending a request to pubs-permissions@ieee.org.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary materials for this paper include:
- detailed numerical results and receiver operation characteristics
- additional results regarding the candidate map filtering procedure,
- more fusion results for realistic forgeries,
- more fusion results for synthetic forgeries,
- confusion matrices for the adopted SVM classifier.
The archive is available for download here: 2016-tip-multi-scale-fusion-supplement.zip (19 MB)
Source Code (Fusion)
An extended version of the proposed random field-based fusion has been implemented in a multi-scale localization toolbox available for download from github.com. The enhanced method can exploit the content of the tampered image to improve shape detection. The algorithm has been described in detail in:
- P. Korus and J. Huang, Multi-scale Analysis Strategies in PRNU-based Tampering Localization, IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017
Source Code (Detector)
A Matlab implementation of the utilized JPEG forgery detector is available from github.com. The detector delivers competetive peformance compared with state-of-the-art alternatives. Detailed experimental evaluation can be found in:
P. Korus, Large-Scale and Fine-Grained Evaluation of Popular JPEG Forgery Localization Schemes, arXiv:1811.12915, 2018